The wound reconstruction is needed after excising a skin cancer, the surgeon deals with a primary defect created by the wound itself, as well as a secondary defect created by the incision. The characteristics of the skin used in a wound reconstruction should match in texture, color, thickness, vascularity, mobility/elasticity, pore size and type of hair. Local flaps are commonly used for defects that are adjacent to the donor site. The types of local flaps are based on the predominant type of movement.
Types of Flaps
- Advancement flaps: the tissue slides entirely in one direction, without rotation or transposition. Advancement flaps are useful when the incision lines of the flap run parallel to existing skin lines.

Before Surgery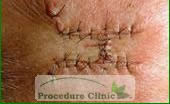
After Surgery - Rotation flaps: designed like a half-circle, with a flap to defect ratio of 3 or 4 to 1, can be used in wound reconstruction in the temple, cheek, scalp, nose and chin; whether rotation flaps are suitable depends on the size of the wound, the extensibility of the donor tissue and the amount of tension that can be tolerated across the secondary defect.
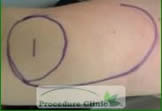
Before Surgery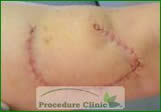
After Surgery - Rhomboid flaps: constructed by designing a rhombus around the primary defect, may be used to redistribute tension on the wound closure.
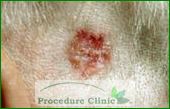
Before surgery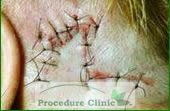
After surgery - V to Y flaps: constructed by designing a V shape skin flap around the primary defect, the secondary defect was closed at the distal part, which turns the closed wounds into Y shape.
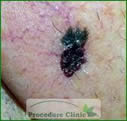
Before surgery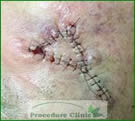
After surgery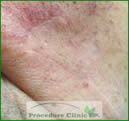
Healed




