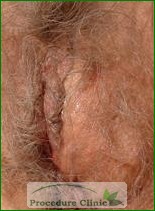
Bartholin’s glands are two round, pea-sized glands at the entrance of the vagina which lubricate the external skin and the tissues at the entrance. If tissue inflammation and injury cause duct blockage, the fluid produced in the gland will accumulate to form a cyst.
If Bartholin’s cyst gets infected, you will feel pain while sitting or walking. The tissues at the entrance to the vagina may become swollen and bleed. However, the abscess may drain by itself after a few days, but you should probably see your doctor right away.
If Bartholin’s cyst is small and painless. They may not need treatment. You’ll probably be advised to take warm sitz baths to try to make the cyst disappear. Antibiotics may be required if you have an infection. Women over 40 may have the cysts removed because of cancer concerns.
Treatment options
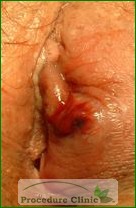
- Open the enlarged gland and drain it, but the swelling may come back later.
- Remove the entire gland, but this is a complicated method with frequent bleeding complications.
- Another choice is to open the gland and insert a special balloon for 4 to 6 weeks, creating a scar tract that prevents the gland duct from blocking again. Some women do not like this method.
- The most common and reliable surgery is marsupialization. This is where the top of the gland is removed, and the skin edges are stitched to the walls of the gland. As this wound heals, the gland shrinks, and the duct is forced to remain open.




